Preventing Respiratory Diseases in Livestock Through Air Filtration
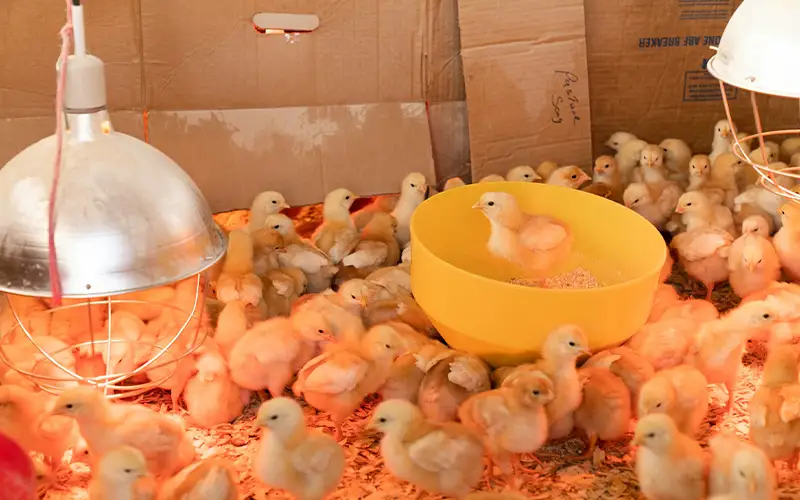
Maintaining high air quality in livestock farming is essential for ensuring the health and productivity of animals. Good air quality helps to prevent the buildup of harmful pollutants like dust, ammonia, and pathogens, which can cause stress and respiratory issues.
By promoting better respiratory health, clean air contributes to healthier animals, improved growth rates, and overall farm productivity. It also enhances animal comfort, leading to better performance and well-being.
Understanding Respiratory Diseases in Livestock
Common Respiratory Diseases Affecting Livestock
Respiratory diseases are a major concern in livestock farming and can affect various species, including cattle, pigs, poultry, and sheep. Some of the most common respiratory diseases include:
Pneumonia: A serious lung infection that can be caused by bacteria, viruses, or fungi. It leads to inflammation and fluid accumulation in the lungs.
Bronchitis: Inflammation of the bronchial tubes, often resulting from viral infections, that leads to coughing and breathing difficulties.
Infectious Bovine Rhinotracheitis (IBR): A viral disease affecting cattle, causing fever, nasal discharge, and severe respiratory distress.
Swine Influenza: A viral respiratory disease in pigs, leading to coughing, fever, and reduced growth rates.
Chronic Respiratory Disease (CRD) in Poultry: Caused by Mycoplasma gallisepticum, this disease leads to coughing, nasal discharge, and poor feed conversion.
Symptoms and Consequences of Poor Air Quality on Livestock Health
Poor air quality in livestock facilities can lead to a range of respiratory issues, significantly impacting animal health and farm productivity. Common symptoms of respiratory diseases caused by poor air quality include:
Coughing and Sneezing: Frequent coughing and sneezing are early signs of respiratory distress.
Nasal Discharge: Clear or colored nasal discharge can indicate infection.
Labored Breathing: Difficulty in breathing, often accompanied by wheezing or gasping.
Reduced Appetite and Weight Loss: Affected animals may eat less and lose weight, leading to poor growth rates.
Lethargy: Decreased activity levels and overall weakness.
The consequences of poor air quality extend beyond immediate health issues. Respiratory diseases can lead to:
Increased Veterinary Costs: Frequent medical interventions and treatments become necessary.
Higher Mortality Rates: Severe respiratory diseases can result in increased animal deaths.
Decreased Productivity: Sick animals have lower growth rates and reduced productivity, impacting overall farm profitability.
Spread of Diseases: Poor air quality can facilitate the spread of infectious agents, affecting more animals on the farm.
Role of Air Filtration in Preventing Respiratory Diseases

How Air Filtration Systems Work
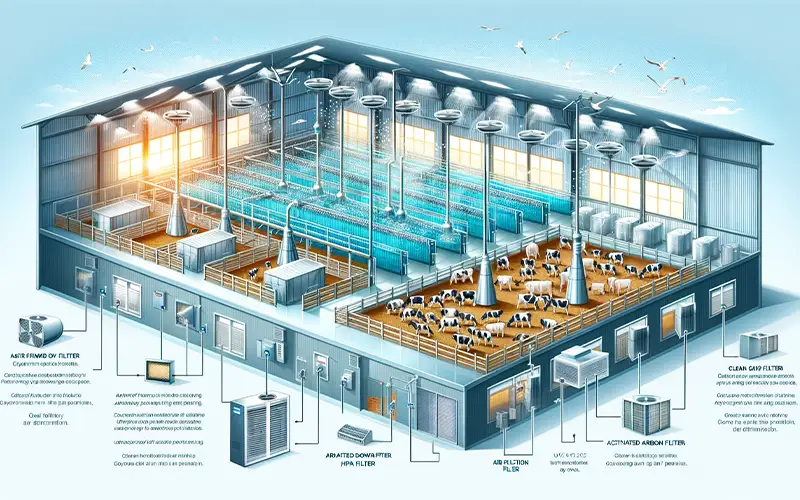
Air filtration systems are designed to remove contaminants from the air, ensuring a cleaner and healthier environment. These systems work by drawing air through various types of filters that trap and neutralize harmful particles and pollutants. Here’s a brief overview of how they function:
Pre-Filters: These capture larger particles like dust and hair, preventing them from clogging the more sophisticated filters.
HEPA Filters: High-Efficiency Particulate Air (HEPA) filters are capable of trapping particles as small as 0.3 microns, including bacteria, mold spores, and dust mites.
Activated Carbon Filters: These filters absorb gases and odors, such as ammonia and volatile organic compounds (VOCs), which are common in livestock environments.
By employing a combination of these filters, air filtration systems effectively reduce the concentration of harmful particles and pollutants, providing a cleaner and safer environment for livestock.
Benefits of Using Air Filtration in Livestock Facilities
Implementing air filtration systems in livestock facilities offers numerous benefits that directly contribute to the health and productivity of the animals:
Reduced Risks of Respiratory Diseases: By removing dust, pathogens, and harmful gases from the air, filtration systems significantly lower the risk of respiratory infections and diseases. This leads to healthier livestock and fewer medical interventions.
Improved Animal Welfare: Cleaner air contributes to better overall health and comfort for the animals. This can lead to improved growth rates, higher feed efficiency, and better reproductive performance.
Enhanced Productivity: Healthy animals are more productive. By reducing the incidence of illness, air filtration helps ensure that livestock remain active and growing, leading to increased productivity and profitability for the farm.
Lower Veterinary Costs: With fewer respiratory illnesses and infections, the need for medical treatments and veterinary interventions decreases, resulting in cost savings for the farm.
Better Environmental Conditions: Air filtration systems help maintain a more stable and comfortable environment within livestock facilities, reducing stress on the animals and improving their overall well-being.
Reduced Spread of Contagious Diseases: Effective air filtration can help prevent the spread of airborne diseases within the facility, protecting not only individual animals but the entire herd or flock.
Implementing Air Filtration Systems in Livestock Facilities
Steps to Assess and Improve Air Quality
Implementing an effective air filtration system begins with a thorough assessment of the current air quality in your livestock facilities. Here are the key steps to follow:
Conduct an Air Quality Assessment:
Identify Pollutants: Determine the types of pollutants present in your facility, such as dust, ammonia, and pathogens. This can be done through air quality testing using specialized equipment or by consulting with environmental health professionals.
Measure Current Levels: Use air quality monitors to measure the concentration of pollutants and compare them against recommended standards for livestock health.
Evaluate Ventilation Systems: Assess the effectiveness of existing ventilation systems in controlling air quality. Check for any blockages or inefficiencies that may be compromising air flow.
Analyze Environmental Conditions:
Temperature and Humidity: Ensure that temperature and humidity levels are within optimal ranges for the specific type of livestock. Both factors can influence the effectiveness of air filtration and the overall health of the animals.
Air Flow Patterns: Study the air flow patterns within the facility to identify areas with poor circulation or stagnant air, which can exacerbate air quality issues.
Develop an Improvement Plan:
Set Goals: Based on the assessment, set clear goals for air quality improvement. These may include reducing specific pollutants to certain levels or improving overall air flow.
Identify Solutions: Research and identify suitable air filtration technologies and strategies to address the specific needs of your facility.
Choosing the Right Air Filtration System for Your Farm
Selecting the appropriate air filtration system is crucial for achieving the desired improvements in air quality. Consider the following factors when choosing a system for your farm:
Understand Your Needs:
Type of Livestock: Different types of animals have varying sensitivities to air quality. For example, poultry may require different filtration solutions compared to cattle or swine.
Specific Pollutants: Identify the primary pollutants you need to address, such as dust, ammonia, or pathogens. This will help you choose a system that targets these specific contaminants effectively.
Evaluate Filtration Technologies:
HEPA Filters: Ideal for capturing fine particles and microorganisms. Suitable for facilities dealing with high levels of dust and pathogens.
Activated Carbon Filters: Effective in absorbing gases and odors, making them ideal for environments with high levels of ammonia or VOCs.
Consider System Capacity:
Size of the Facility: Ensure that the air filtration system you choose can handle the volume of air in your livestock facility. Larger facilities may require more powerful or multiple filtration units.
Air Exchange Rate: Look for systems with an appropriate air exchange rate to ensure that the air within the facility is being filtered at a rate that maintains healthy air quality levels.
Assess Maintenance Requirements:
Filter Replacement: Choose systems with easily replaceable filters and consider the cost and frequency of filter replacements.
System Durability: Opt for robust systems designed to withstand the specific conditions of your livestock facility, ensuring long-term reliability and efficiency.
Consult with Experts:
Professional Advice: Work with air quality experts or consultants who can provide tailored recommendations based on your specific needs and conditions.
Manufacturer Support: Engage with reputable air filter manufacturers who offer support and guidance in selecting and installing the right system.
Conclusion
Air filtration plays a crucial role in maintaining high air quality within livestock facilities, directly impacting animal health and productivity.
By effectively removing harmful pollutants such as dust, ammonia, and pathogens, air filtration systems significantly reduce the risk of respiratory diseases. Healthy air quality leads to healthier animals, fewer medical interventions, and better overall farm performance.
Investing in air filtration systems is an essential step towards ensuring the well-being of your livestock. Healthier animals are more productive and require less veterinary care, ultimately leading to increased profitability.
By prioritizing air quality, you create a safer and more comfortable environment for your animals, supporting their growth and maximizing the success of your farming operation. Take the initiative to implement effective air filtration solutions and witness the benefits of healthier, more productive livestock.












